GST
GST Registration
Get in Touch

Growing Business
Finance Helps You To Convert Into A Strategic Asset Get.
Finance Investment
Finance Helps You To Convert Into A Strategic Asset Get.
Tax Advisory
Finance Helps You To Convert Into A Strategic Asset Get.
GST Registration
Goods and Services Tax (GST) registration is a mandatory process for businesses in India engaged in the supply of goods or services. GST is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services throughout India, replacing multiple indirect taxes like service tax, excise duty, and value-added tax (VAT).
Overview of Online GST Registration
Since its introduction on 1 July 2017, the Goods & Services Tax (GST) has been mandatory for all service providers, traders, manufacturers, and even freelancers in India. The GST system was implemented to replace Central and state-level taxes such as Service Tax, Excise Duty, CST, Entertainment Tax, Luxury Tax, and VAT, making the tax process more streamlined.
For those taxpayers whose annual turnover is less than 1.5 crore, the GST framework provides an option for a composition scheme. This scheme allows them to undergo simplified GST procedures and pay taxes at a predetermined rate according to their turnover.
The GST mechanism operates throughout various stages of the supply chain. This includes acquiring raw materials, production, wholesale, retail, and the eventual sale to the end consumer. Notably, GST is imposed at every one of these steps. For example, when a product is produced in West Bengal and then used in Uttar Pradesh, the GST revenue generated is allocated entirely to Uttar Pradesh, emphasizing the consumption-based nature of GST.
Key Components of GST
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India is structured around three primary components:
Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST): This tax is levied by the Central Government on the supply of goods and services within a particular state. CGST applies to transactions carried out entirely within the boundaries of one state.
State Goods and Services Tax (SGST): SGST is charged by the State Government on the supply of goods and services within its jurisdiction. Similar to CGST, SGST is also limited to transactions happening within a specific state.
Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST): This tax is imposed by the Central Government on the supply of goods and services that occur between different states or between a state and a Union Territory. IGST is relevant for transactions where goods or services cross state or Union Territory boundaries.
Who is Required to Register for GST?
GST registration is essential for the following person:
Business Entities: Any enterprise with an aggregate annual turnover exceeding Rs. 40 lakhs. For special category states under GST, the threshold is Rs. 20 lakhs.
Service Providers: Those with an aggregate annual turnover surpassing Rs. 20 lakhs. For special category states, this limit is Rs. 10 lakhs.
Exemptions: It’s important to note that entities dealing exclusively in GST-exempted goods or services are not bound by these thresholds.
Previously Registered Entities: Entities that were registered under older tax frameworks (like Excise, VAT, Service Tax, etc.) need to migrate and register under the GST regime.
Inter-State Suppliers: Any entity or individual involved in the supply of goods across state boundaries.
Casual Taxable Entities: Those who undertake taxable supply occasionally.
Entities under Reverse Charge Mechanism: Businesses are obligated to pay tax under the reverse charge.
Input Service Distributors & Agents: Distributors of input services, including their representatives.
E-Commerce Platforms: Operators or aggregators of e-commerce platforms
Non-Resident Taxable Entities: Individuals or entities that are non-resident but engage in taxable supply within India.
Supplier’s Agents: Representatives who supply on behalf of a principal supplier.
E-Commerce Suppliers: Individuals or entities that offer goods or services through an e-commerce aggregator.
Online Service Providers: Entities delivering online information, database access, or retrieval services from outside India to an individual in India, excluding those already registered under GST.
GST Registration Turnover Limit
GST registration can be obtained voluntarily by any person or entity irrespective of turnover. GST registration becomes mandatory if a person or entity sells goods or services beyond a certain turnover.
Service Providers: Any person or entity who provides service of more than Rs.20 lakhs in aggregate turnover in a year is required to obtain GST registration. In special category states, the GST turnover limit for service providers has been fixed at Rs.10 lakhs.
Goods Suppliers: As per notification No.10/2019 any person who is engaged in the exclusive supply of goods whose aggregate turnover crosses Rs.40 lakhs in a year is required to obtain GST registration. To be eligible for the Rs.40 lakhs turnover limit, the supplier must satisfy the following conditions:
- Should not be providing any services.
- The supplier should not be engaged in making intra-state (supplying goods within the same state) supplies in the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Pondicherry, Sikkim, Telangana, Tripura and Uttarakhand.
- Should not be involved in the supply of ice cream, pan masala, or tobacco.
If the above conditions are not met, the supplier of goods would be required to obtain GST registration when the turnover crosses Rs.20 lakhs and Rs.10 lakhs in special category states.
Special Category States: Under GST, the following are listed as special category states – Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Jammu and Kashmir, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
Aggregate Turnover: Aggregate turnover = (Taxable supplies + Exempt Supplies + Exports + Inter-State Supplies) – (Taxes + Value of Inward Supplies + Value of Supplies Taxable under Reverse Charge + Value of Non-Taxable Supplies).
Aggregate turnover is calculated based on the PAN. Hence, even if one person has multiple places of business, it must be summed to arrive at the aggregate turnover.
Advantages of GST Registration for Businesses
- Legitimacy and Credibility: GST registration provides legal recognition to a business, enhancing its legitimacy and credibility in the market.
- Access to Input Tax Credit: Registered businesses can claim the input tax credit, allowing them to offset the GST paid on purchases against the GST collected on sales, reducing overall tax liability.
- Interstate Transactions: GST registration is mandatory for businesses involved in interstate transactions, enabling them to engage in legal and compliant interstate trade.
- Market Expansion: GST registration facilitates business expansion by enabling participation in the formal economy and making it easier to establish a presence in multiple states.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses with GST registration may have a competitive advantage over non-registered counterparts, as many entities prefer to deal with registered suppliers.
- Legal Compliance: Compliance with GST regulations, including timely filing of GST returns and maintaining proper records, helps businesses avoid penalties and legal issues.
- Composition Scheme Option: Small businesses with a turnover below a specified limit have the option to opt for the Composition Scheme, simplifying compliance requirements.
- Online Presence and Visibility: GST registration provides an online presence through the GST portal, offering visibility to businesses and making them discoverable by potential customers.
- Ease of Doing Business: GST replaces multiple indirect taxes, reducing the complexity of taxation and making it easier for businesses to understand and comply with tax requirements.
- Government Tenders and Contracts: Many government tenders and contracts require GST registration, allowing registered businesses to participate in government procurement processes.
- Input Tax Credits on Capital Goods: Businesses can claim the input tax credit on the purchase of capital goods, providing a cost-saving advantage.
- Streamlined Taxation System: GST simplifies the taxation system by eliminating cascading effects and promoting a more transparent and efficient tax structure.
- Reduced Tax Burden on Consumers: The implementation of GST aims to reduce the tax burden on consumers by eliminating hidden taxes and promoting a more uniform tax structure.
GST Certificate
The GST Certificate stands as an authoritative document provided by the Indian government to entities that are registered under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework. This certificate confirms a business’s legitimate Registration under GST and prominently displays key details such as the GST identification number, the business name, and the official address.
Possessing an authentic GST Certificate is pivotal for enterprises because:
- Tax Collection Authority: It empowers businesses to impose and gather GST from their clientele.
- Tax Credit Claims: With this certificate, businesses can rightfully claim credits on the GST they’ve disbursed on their procurements and operational costs.
Furthermore, beyond its tax-related functions, the GST Certificate holds significance in several other domains:
- Loan Applications: When seeking financial aid or loans, businesses might be asked to present their GST certificates to validate their authenticity.
- Government Tenders: To be eligible and participate in official government tenders, the GST Certificate must often be produced as evidence of tax compliance.
- Market Reputation: The certificate enhances a business’s stature in the market, reflecting its commitment to national tax regulations.
GSTIN
GSTIN, which stands for Goods and Services Tax Identification Number, is a distinctive 15-digit alphanumeric code allocated to every taxpayer who is registered under the GST framework in India. This number acts as the primary identifier for both businesses and individuals in the context of GST-related transactions and compliance.
GST return filing
GST return filing is a formal process in which a taxpayer provides the government with information regarding their sales, purchases, and taxes collected and disbursed. In India, every GST-registered taxpayer must submit these returns consistently, even if there were no sales or purchases during a particular period.
If you need assistance, our team of experts is at your service to guide you through the GST return filing process.
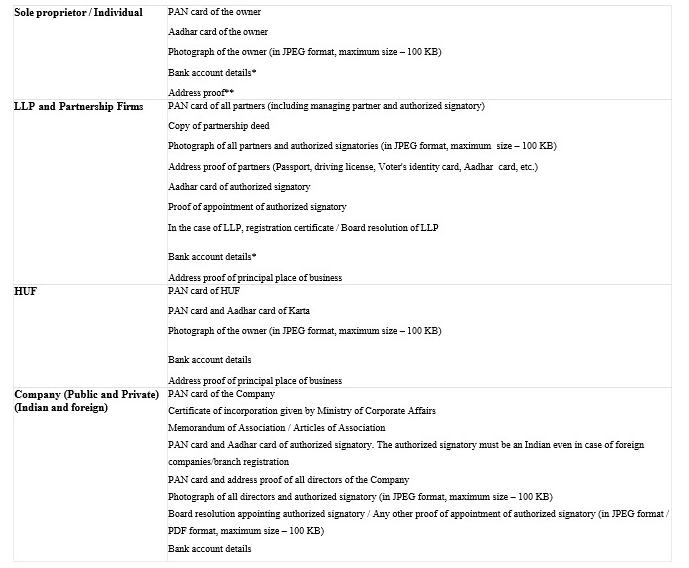
Consequences of Not Securing GST Registration
For Non-Payment or Underpayments: If a taxpayer either neglects to pay the requisite tax or mistakenly underpays, an acceptable equivalent of 10% of the outstanding tax amount is levied. However, the penalty cannot be less than Rs. 10,000.
Intentional Tax Evasion: If an individual or business wilfully avoids paying the due taxes, the penalty equals 100% of the evaded tax amount.
GST Registration quickly through FinHub Advisors Pvt Ltd
Experience a swift and efficient process for your GST registration with the expert assistance of FinHub Advisors Pvt Ltd. Our dedicated team streamlines the entire journey, ensuring a hassle-free experience for your business. From comprehensive consultation to precise documentation assistance, we handle the intricacies of the application process. With FinHub Advisors Pvt Ltd, you can trust timely submission, proactive follow-ups, and regular updates on your registration status. Let us navigate the complexities, providing expert guidance and ensuring that your GST registration is seamlessly completed, allowing you to focus on your business operations with confidence.